
Viz.ai Announces Agreement with Bristol Myers Squibb to Enable Earlier Detection and Management...
Viz.ai has submitted a de novo classification request to the FDA for a new AI algorithm intended to identify and...
Mar 02, 2023
Apr 24, 2025
4 minutes
By Jamie Stern, MBA, Senior Director, Clinical Operations & Strategy at Viz.ai

Healthcare AI integrated into clinical workflows isn’t skipping a beat in cardiovascular care—it’s helping clinicians catch conditions that might otherwise go undiagnosed for years. One of the most compelling use cases is in the AI-powered analysis of electrocardiograms (ECGs). These everyday, low-cost tests are being transformed into powerful tools for early disease detection. When paired with smart algorithms and clinician-friendly workflows, ECGs can reveal critical insights that can be hard to detect.
One standout example is Viz HCM, an AI-enhanced ECG solution developed to detect the signs of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)—a subtle but serious inherited heart condition that often evades traditional diagnostic approaches. In 2023, Viz.ai in partnership with a top tier pharma company developed and deployed Viz HCM to help identify and triage patients with signs of HCM. Trained on a diverse dataset of over 831,000 ECGs from more than 300,000 patients, Viz HCM leverages a multilayer convolutional neural network to find those underlying signals of HCM.
Today, the data is putting heart behind the hype: real-world studies show that this AI-driven approach doesn’t just look good on paper—it’s delivering in practice, helping clinicians identify more patients, earlier, and with greater precision.
Viz HCM can be applied to ECGs from general patient populations being evaluated at hospitals, without prior suspicion of HCM. This allows for the identification of unrecognized HCM patients who might not have been diagnosed through traditional clinical pathways. Published in Heart, one prospective study across 5 centers identified new HCM patients through AI-based alerts on ECGs using Viz HCM, with 7.8% of enrolled patients receiving a new HCM diagnosis out of 217 enrolled patients [1]. Viz HCM also advances the workflow by triggering further clinical assessment. The median time from ECG to diagnostic imaging indicating HCM in this study was 7.5 days.
Another recent study highlights the real-world impact of Viz HCM in everyday cardiology workflows. Published in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology and presented live at ACC.25 by Dr. Milind Desai, Director of the Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Center at Cleveland Clinic [2]. The researchers evaluated Viz HCM’s ability to detect both known and previously undiagnosed cases of HCM using AI-enhanced 12-lead ECG analysis across nearly 46,000 adult patients.
Key findings included:
Among those flagged:
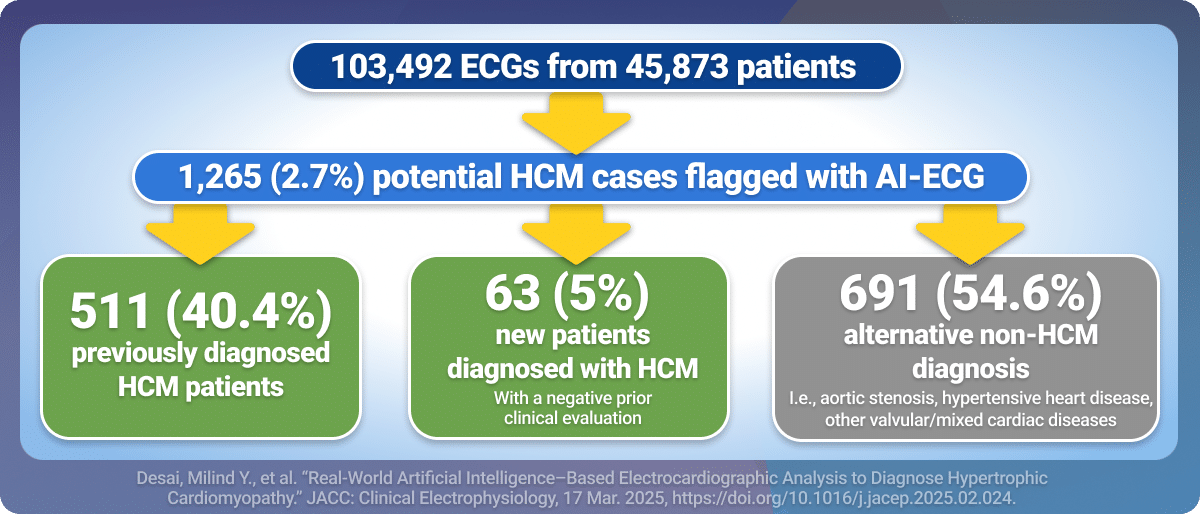
These findings suggest that Viz HCM serves as a valuable screening tool that can augment current care pathways by flagging individuals with potential HCM who may not have been previously diagnosed. This “safety net” is particularly important given that many HCM patients remain undiagnosed, which can have substantial clinical and familial implications. But the value doesn’t stop there—surfacing known HCM patients also represents a currently missed clinical and economic opportunity, especially for hospitals that are not yet Centers of Excellence (COE) but are working toward designation in the coming years. By identifying both new and existing patients, Viz HCM can help these institutions improve patient capture, streamline pathways to diagnosis, and enable earlier management that ultimately improves outcomes.
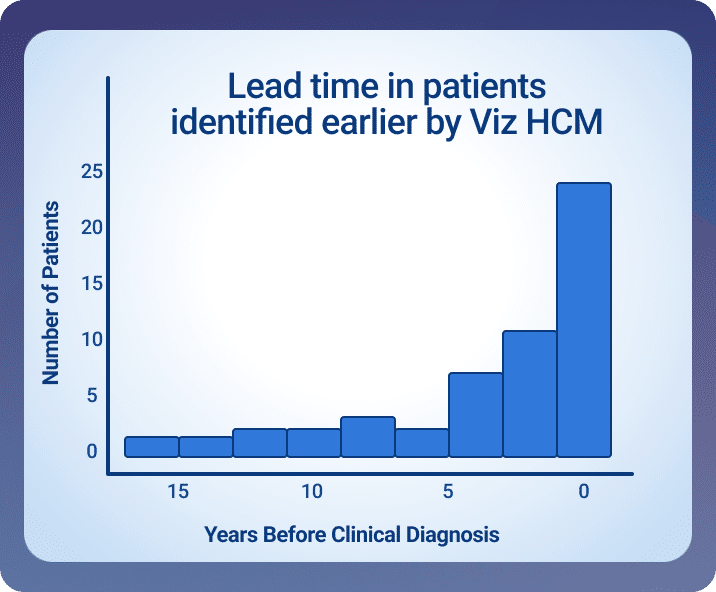
By improving the detection rate, Viz HCM can enable earlier management of HCM. AI-ECG is a fast, inexpensive, and widely used tool to initiate screening for cardiac conditions. Patients flagged by AI-ECG, such as Viz HCM, can then receive more extensive imaging to help accelerate the diagnostic process. One pivotal study, presented by the University of Virginia, took a retrospective look at how Viz HCM might have shifted the diagnostic timeline. Presented at ACC.25 by Michael Ayers, MD, Director of the HCM Center of Excellence at the University of Virginia [3], this retrospective, blinded study reviewed 15 years of patient data from UVA’s HCM Center of Excellence.
Of 155 patients who were ultimately diagnosed with HCM:
These findings point to the potential for AI-powered ECG analysis to significantly accelerate time to diagnosis for many patients, leading to earlier treatment and improved patient outcomes in a progressive disease like HCM.
HCM affects as many as 1 in 500 people, yet up to 85% of cases remain undiagnosed or misdiagnosed. This is despite the fact that over 90% of HCM patients show abnormalities on ECGs. The challenge lies in the limitations of traditional ECG interpretation, which often lacks the specificity needed to flag HCM among other cardiac conditions.
The Cleveland Clinic, UVA, and multi-center studies demonstrate how AI-enhanced ECG analysis can shift this paradigm. As Dr. Milind Desai, Director of the Center for Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy at Cleveland Clinic, explains:
“It’s exciting to see the growing real-world evidence showing how AI-enhanced ECG analysis can play a pivotal role in identifying new patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy,” said Milind Desai, MD, MBA. “By leveraging AI as a second set of eyes, we can expand the ability to diagnose more HCM patients earlier and across diverse populations, tackling a condition that’s often challenging to detect.”
By transforming a widely available, low-cost tool like the ECG, Viz HCM makes earlier and more accurate detection not only possible—but also scalable.
These results are the product of a powerful collaboration between Viz.ai, leading researchers, and life sciences partners—a model that brings together technological innovation and deep clinical insight. From design and deployment to real-world validation, Viz HCM was built with the goal of meeting an urgent clinical need and improving patient outcomes at scale. Viz HCM is now in 95 hospitals, and is on track to expand to approximately 200 by the end of 2025.
Looking ahead, the success of Viz HCM lays the foundation for expanding AI-powered solutions into other underdiagnosed cardiovascular conditions, such as transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy (ATTR-CM), atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), atrial fibrillation (aFib), and resistant hypertension. By applying the same approach—clinical collaboration, real-world deployment, and rigorous validation—there’s potential to help more patients get diagnosed earlier and start treatment sooner. If we can detect HCM earlier with AI, what’s stopping us from transforming the entire landscape of cardiovascular care?
Press Release on the recent HCM studies presented at ACC.25